In this article you will read about The physical features of India. It also includes Indian Geography Map, various parts of India geography.
Our country is vast in the world. The physical features of India are expanded on all sides.
Geography of India or the geographical nature of India refers to the distribution of geographical elements in India and its pattern, which is quite diverse in almost every respect.
‘The Physical Features of India’ with Indian Geography Map
Indian Geography Map
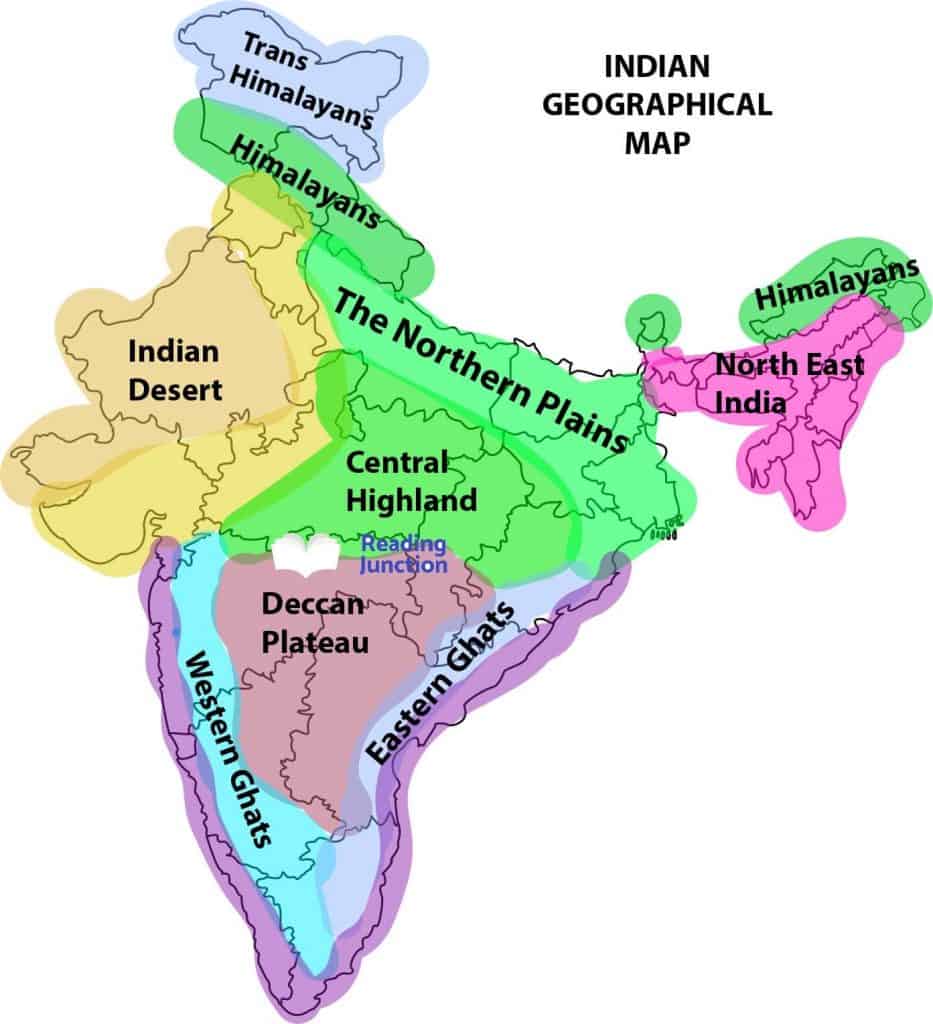
The Indian Subcontinent
The world power is surprised and jealous of seeing the physical geography of India. Situated on the intermediate peninsula of the three peninsulas of South Asia, this country is the seventh-largest country in the world, with an area of 32, 26,283 sq km.
The Indian subcontinent can be separated into the accompanying parts.
- The incredible mountains
- Incredible Northern Plain
- The Peninsular Plateau
- Incredible Desert of India
- Beachfront Plain
- Islands
1. The incredible mountains
Himalaya is one of the geographical features in India, which is world-famous. Himalaya is the most elevated mountain on the planet, situated in the northern fringe of India. It reaches out from the Naga Mountains (Pakistan-controlled Kashmir) to Namcha Barwa (Tibet).
It is 2500 km (15.50 mi) long from west to east and has a normal width of 200 to 400 km. Mount Everest (Nepal) is its littlest.
More noteworthy Himalaya or Himadri The more prominent Himalaya (Himadri)
The normal height of Himadri is 1600 feet (4900 m). It is the tallest of the three pieces of the Himalayas. Mount Everest is situated in this part.
Mount Everest, China-Nepal fringe (tallness 8850 m or 29035 ft), Kanchenjunga, Sikkim (stature 8586 m or 28169 ft), Nanda Devi (tallness 7817 m or 25646 ft), Kamet (stature 7755 m 25256 ft), Trishul (stature 7120 m 23359 ft).
These three are situated in Uttaranchal. The Great Himalayas are generally secured with a day off; of the Himalayan icy masses are found in this part.
2. Incredible Northern Plains
There is a huge area that comes on the north side, which is shown in the Indian physical map. The incredible northern plain locale is isolated into three fundamental parts-
1. Fields of Punjab and Haryana
2. Gangetic Plain
3. Brahmaputra Plains
Sutlej, Ganga, and Brahmaputra go under it. It is the most prolific and thickly populated territory on the planet. This territory is made of shuddering soil.
Western plain
This is the Indus or Sutlej Plain. The Indus, Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi waterways, for the most part, stream in this plain.
Eastern plain
The eastern plain is known as the Gangetic plain, and it is isolated into two sections viz: ‘Bangar and Khadar’. Where rising water doesn’t arrive at it is called Bangar, and where rising water gathers new soil each year, it is called Khadar.
The expansion of the Bangar plain is situated in Uttar Pradesh and the augmentation of Khadar in Bihar and Bengal.
Bhanbhar Pradesh
Where the Himalayan Mountains and Sutlej Ganges Plain meet, this region is called Bhanbhar. The part secured with Kankar stones brought by countless streams depleting from the Himalayan district is called Bhambhar.
Trees with long roots are found here. However, little plants are regularly discovered ailing in fields and populace.
Tarai locale
The lower locale of Bhanbhar is Terai in this part, for the most part, Dakadak and high punch like elephant penetrating, Kans Bhanbhar bison were found.
3. The Peninsular Plateau
Peninsular India or Deccan is the name of the land that broadens south of the northern India plain. Which is encircled on three sides by the ocean? It is partitioned into two sections
1. Malwa Plateau
2. Deccan Plateau
Malwa Plateau
The progression breaks the Malwa level of waterways. In this part, on the eastern side of Baghelkhand and west of Bundelkhand, rough waterways are constructed. Vindhyachal slopes, Gwalior slopes are found in this part. Satpura, Amarkantak, Chota Nagpur level, Rajmahal slopes, and so on are found under the Malwa level.
Ranchi, Hazaribagh, Singhbhum, Palamu, Lohardagga, and so forth are secured under the Chhotanagpur level. In this level, numerous profound waterways Mahanadi, Son, and Suvarnarekha stream are found. This level is extremely plentiful in minerals, and 60% mica, and the greater part of the iron is gotten here.
Sinhbhoomi May gives iron and chromite, and Chota Nagpur Plateau gets Kavelin (mud), tungsten, limestone, quartz, coal and copper, and so on. Chhota Nagpur Plateau is otherwise called “Mineral Resources Store”.
Satpura Mountains Is a break valley of the Tapi stream. Tapi and Narmada stream from these break valleys, these waterways slide from the levels and structure numerous cascades. The Smogadhar cascade of the Narmada River close to Jabalpur is a prime case of this.
It has the best white marble rocks. Both the Narmada and Tapi streams stream against the overall incline of the level, because of the deficiency where it streams. Their angle is from east to west.
Airways slopes are the most noteworthy little Guru slopes in the district. As per a few researchers, this is the most established mountain on the ground, which despite of everything exists.
Deccan Plateau
This spring of gushing lava is made out of extricated magma, which is well known for cotton development.
Mysore or Karnataka Plateau
It is plentiful in minerals. A large portion of the best coal in India is found here.
Chhattisgarh Lowland (Gharjat Pahadia)
Chhattisgarh fields are conspicuous in it, which is additionally called rice bowl. The Narmada falling in the Arabian Sea, the child found in the Ganges, the Mahanadi streaming towards the Bay of Bengal, all begin from this district.
Dandakaranya level area
The majority of its territory is secured with backwoods. This is an innate, overwhelmed zone, with iron metal being the prevailing region.
Western Ghats
Here the slopes of Sahyadri are found. Rail and thruways have gone through two significant passes Thalghat and Borghat. From this, Krishna, Bhima, Godavari, Tungabhadra streams stream out and stream towards the east.
Mahabaleshwar is a popular wellbeing advancing spot in Maharashtra close to Krishna’s starting point. The most noteworthy top here is Anaimudi, and Doddabetta is the second most elevated pinnacle.
The Western Ghats are near the ocean. Numerous cascades have risen up out of its streams, for example, the Shivasamudram Falls (100 m) of the Cauvery River, the Gokak Falls (55 m) of the Gokak River, the Gurusoppa of the Sarasvati River or the Mahatma Gandhi Falls (the most noteworthy cascade in India is 250 m), Mahabaleshwar. Of Yena Falls (183 m) are found.
The Western Ghats have Nilgiri slopes (Palani, Annamalai, and Cardamom slopes).
Eastern Ghats
Nallabamalai, Palakonda, Javadi, Shivaratri, and different slopes come. Mahendragiri (1501 m) is its most elevated slope.
4. Great Desert of India
Thar Desert
Indian desserts are the main recognition of the physical geography of India. Approx 644 km Long and 360 km is wide. It is assessed that it is moving towards Agra and Mathura in western Uttar Pradesh.
Saurashtra and the Rann of Kutch
It is around 322 km long and 161 km wide, in which just the region of the slopes of Girnar is fruitful.
5. Beachfront Plain or the seaside plain
The beachfront plain is spread in two sections, the eastern and western seaside fields.
Western Coastal Plain
These incorporate the beachfront plain of Gujarat, seaside plain of Konkan, waterfront plain of Karnataka (Mysore), waterfront plain of Malabar.
East Coast Plains
Its lower part is called the Coromandel Coast. The lower some portion of which is the delta of Krishna, Godavari, and Cauvery streams, this is called Coromandel Coast, it is a fruitful zone. It has three sections –
Utkal Coastal Plain– It is along the bank of Orissa. Chilka Lake is situated here; flowing backwoods are spread in the delta of Tanta Mahanadi. Being prolific; rice and jute are developed here.
Coastal fields of Andhra or Kakinara– It comprises of the deltas of Krishna and Godavari. Visakhapatnam, Kakinada, and Masulipatnam are the significant ports on this coast.
Coastal piece of Tamil Nadu or Coromandal– This part is, for the most part, made fruitful by the Kaveri River. Chennai, Tuticorin, and Nagapattinam are the significant ports here. It is renowned for the lofty thick of Mannar.
6. Islands
It comprises of Lakshadweep and Andaman and the Nicobar Islands. Lakshadweep is a gathering of 36 coral islands, and Nicobar is a gathering of 324 islands.
The 10-degree channel isolates Andaman and Nicobar. The 10-degree scope line goes through here.
Final Worlds
After a deep analysis of 6 physical features of India, we can reach on to the conclusion that our country has lots of God’s gifted heritage. It can be seen clearly in Indian physical map that borders of country touch the boundaries of a neighboring county.
We are proud of Indian features and their characteristics and heritage. Our country is the seventh-largest in the world and the second-most populous country in the world.
The Physical features of India are world-famous, where people speak different languages, and people of different castes, religions, sects, and cultures live together.